What Is the CNC Machining Process for Cast Iron Molds? Key Steps and Professional Analysis
🔍 1. Basic Concept of CNC Machining for Cast Iron Molds
CNC machining for cast iron molds refers to the process of performing high-precision cutting, drilling, milling, and other operations on cast iron molds using Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology. Cast iron molds are typically used in manufacturing auto parts, industrial machinery components, etc. Due to their high hardness and excellent wear resistance, they are widely applied in mass production. The core of CNC machining lies in controlling the machine tool through programming to achieve precise fabrication of complex shapes, ensuring that the mold's dimensional accuracy and surface quality meet design requirements.
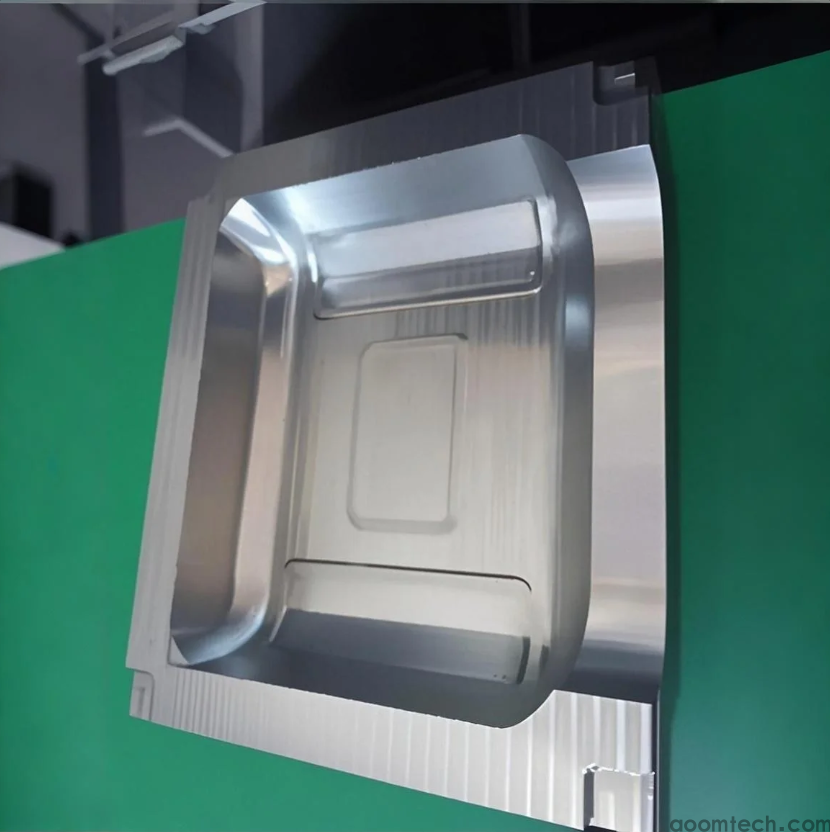
⚙️ 2. Core Process Flow of CNC Machining for Cast Iron Molds
The CNC machining process for cast iron molds consists of multiple refined steps, and each step directly affects the final quality of the mold. Below is a detailed analysis of the key processes:
1. Mold Design and Programming
- Before machining, mold design must be carried out based on product requirements, and CNC machining programs must be generated using CAD/CAM software. Programming needs to consider tool paths and cutting parameters (such as feed rate and cutting depth) to ensure machining efficiency and precision.
2. Material Selection and Preparation
- Common materials for cast iron molds include gray cast iron and ductile iron. The material should be selected according to the mold's requirements for hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. Material preparation involves cutting and rough machining to form a blank that is close to the final shape (near-net shape), thereby reducing the amount of subsequent machining.
3. CNC Rough Machining
- The blank is initially cut using a milling machine or CNC machine tool to remove a large amount of excess material and form the basic shape of the mold. A machining allowance of approximately 0.2mm per side must be reserved during rough machining to prepare for finish machining.
4. Heat Treatment
- To enhance the mold's hardness and wear resistance, heat treatment (such as quenching and tempering) is required. Internal stress may exist after heat treatment, which must be eliminated through aging treatment to prevent deformation during subsequent machining.
5. CNC Finish Machining
- High-precision CNC machine tools are used for fine cutting of key parts (such as mold cavities and hole positions), ensuring that the dimensional accuracy reaches 0.005–0.02mm and the surface finish meets requirements. Finish machining often involves 5-axis machine tools to process complex curved surfaces.
6. Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (Wire EDM) and Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
- For fine features that cannot be directly machined by CNC (such as narrow slots and deep holes), Wire EDM or EDM is used. These technologies can process high-hardness materials and achieve micron-level precision.
7. Polishing and Surface Treatment
- Mechanical polishing or chemical treatment is used to improve surface roughness, especially for molds that require a mirror finish. Polishing must strictly control the area to avoid damaging precision parts.
8. Assembly and Mold Testing
- The machined parts are assembled into a complete mold, and mold testing is conducted. Mold testing verifies the functionality of the mold, such as whether the gating system and cooling water channels work properly. If problems are found, adjustments or repairs are required.
💡 3. Why Is the Process Flow So Important?
The optimization of the process flow directly determines the mold's quality and production efficiency.
- Precision Guarantee: Strictly controlling machining parameters (such as allowance and heat treatment temperature) at each step can avoid defects like deformation and cracks, ensuring the mold's service life and product consistency.
- Cost Control: Reducing material waste through near-net shape casting and lowering labor costs by combining CNC automated machining to achieve efficient production.
- Wide Application: The optimized process is suitable for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical equipment, meeting the manufacturing needs of high-precision components.
🤔 4. Common Problems and Solutions
- Problem 1: Cracks in the mold after machining
→ Cause: Internal stress from heat treatment is not completely eliminated.
→ Solution: Increase aging treatment or perform multiple tempering processes to release internal stress.
- Problem 2: Surface roughness does not meet standards
→ Cause: Improper cutting parameters or tool wear.
→ Solution: Optimize CNC programming, replace tools regularly, and add a polishing process.
- Problem 3: Difficulty in machining complex structures
→ Cause: Limitations of CNC machine tools.
→ Solution: Combine Wire EDM or EDM to process detailed features.
🚀 5. How to Choose a Reliable Machining Service?
For beginners, the following aspects should be considered when choosing a service provider:
- Technical Capability: Whether the provider has advanced equipment such as 5-axis CNC machines and EDM machines.
- Experience Accumulation: Priority should be given to manufacturers specializing in cast iron molds, such as suppliers in the automotive and machinery fields.
- Quality Control: Request precision inspection reports and mold testing results to ensure compliance with standards.
🌟 6. Industry Trends and Personal Insights
In the future, CNC machining for cast iron molds will become more intelligent and green:
- Intelligence: CNC machines integrated with AI and the Internet of Things (IoT) can monitor the machining status in real time, adjust parameters automatically, and reduce human errors.
- Green Manufacturing: Adopting dry cutting or minimal quantity lubrication technology to reduce environmental pollution while lowering costs.
- Personal View: For small and medium-sized enterprises, investing in "three-process integrated" equipment (combining cutting, grinding, and rough machining, for example) can significantly improve efficiency. However, emphasis must be placed on the training of technical personnel to fully exploit the equipment's potential.
✅ 7. Conclusion
The CNC machining process for cast iron molds is a technique that integrates design, materials science, and precision engineering. By strictly following the process, optimizing parameters, and selecting a reliable service provider, even beginners can achieve high-quality mold manufacturing. Remember, precision is the core, and details determine success or failure!
Do you want me to sort out a Cast Iron Mold CNC Machining Process Parameter Checklist? It will help you quickly check whether each key step and parameter meets the standard during the actual machining process.
 How is the price calculated fo
How is the price calculated fo
 How Does a High-Precision CNC
How Does a High-Precision CNC
 What Factors Affect CNC Machin
What Factors Affect CNC Machin
 How to Choose a Supplier for C
How to Choose a Supplier for C


